您现在的位置是:主页 > news > 门户网站建设多久/2024年8月爆发新的大流行病毒吗
门户网站建设多久/2024年8月爆发新的大流行病毒吗
![]() admin2025/5/1 0:31:13【news】
admin2025/5/1 0:31:13【news】
简介门户网站建设多久,2024年8月爆发新的大流行病毒吗,专业网站建设推广,长沙做网站湖南微联讯点靠谱一、HashMap介绍 HashMap是Map接口的一个实现类(HashMap实现了Map的接口),它具有Map的特点。HashMap的底层是哈希表结构。 Map是用于保存具有映射关系的数据集合,它具有双列存储的特点,即一次必须添加两个元素…
一、HashMap介绍
HashMap是Map接口的一个实现类(HashMap实现了Map的接口),它具有Map的特点。HashMap的底层是哈希表结构。
Map是用于保存具有映射关系的数据集合,它具有双列存储的特点,即一次必须添加两个元素,即一组键值对==><Key,Value>,其中Key的值不可重复(当Key的值重复的时候,后面插入的对象会将之前插入的具有相同的Key值的对象覆盖掉),Value的值可重复。
其中<Key,Value>键值对在Java语言中又被称之为Entry/entry,Map.Entry就相当于Student.name,若name的数据类型为String,则Student.name的数据类型为String,同理若<key,value>中key的数据类型为Integer,value的数据类型为String,则Map.Entry的数据类型为<Integer,String>。在HashMap与TreeMap中均可使用Map.Entry。
接下来我们将结合代码来具体学习HashMap相关知识。
二、HashMap的基本操作代码 HashMap入门
Key数据类型为Integer类型,Value数据类型为String类型的HashMap
public static void main(String[] args) {//若要使用HashMap,我们需要导入import java.util.HashMap;//我们使用泛型来约束HashMap的数据类型,Key为Integer数据类型,Value为String数据类型HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();//使用put()方法来添加数据hashMap.put(100, "北京");hashMap.put(99, "上海");hashMap.put(98, "广州");//普通打印输出System.out.println(hashMap);}
运行结果:
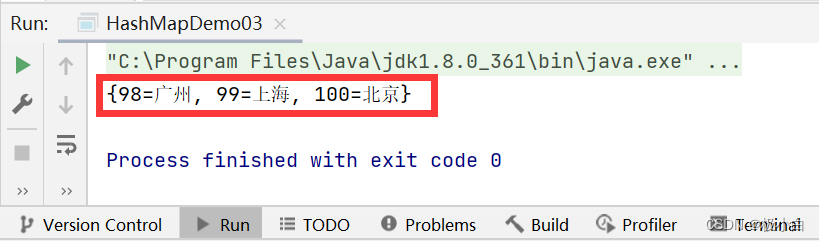
接下来我们探讨Key的值不可重复(当Key的值重复的时候,后面插入的对象会将之前插入的具有相同的Key值的对象覆盖掉),Value的值可重复此问题
Key数据类型为Integer类型,Value数据类型为String类型的Map
其中第一对象和第五对象的Value值相同,第三对象与第四对象的Key值相同。
public static void main(String[] args) {//若要使用HashMap,我们需要导入import java.util.HashMap;//我们使用泛型来约束HashMap的数据类型,Key为Integer数据类型,Value为String数据类型HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();//使用put()方法来添加数据hashMap.put(97, "北京");//第一对象hashMap.put(98, "上海");//第二对象hashMap.put(99, "广州");//第三对象hashMap.put(99, "深圳");//第四对象hashMap.put(100, "北京");//第五对象//打印输出System.out.println(hashMap);}
运行结果:(我们发现后面插入的第四对象将之前插入的第三对象给覆盖掉了,而第一对象与第五对象的Value值重复则不会带来任何影响)
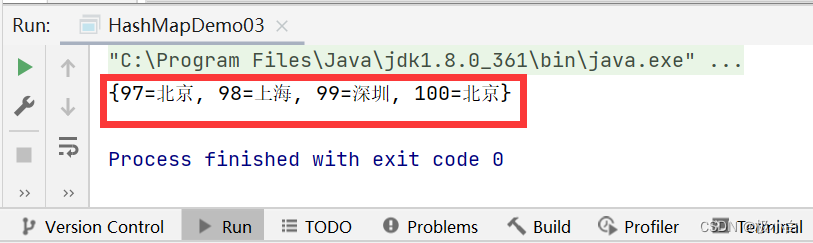
三、HashMap的遍历操作 HashMap基础
HashMap的遍历分为调用keySet()方法遍历和entrySet()方法遍历
HashMap调用keySet()方法遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {//若要使用HashMap,我们需要导入import java.util.HashMap;//我们使用泛型来约束HashMap的数据类型,Key为Integer数据类型,Value为String数据类型HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();//使用put()方法来添加数据hashMap.put(97, "北京");//第一对象hashMap.put(98, "上海");//第二对象hashMap.put(99, "广州");//第三对象hashMap.put(99, "深圳");//第四对象hashMap.put(100, "北京");//第五对象//调用keySet方法遍历//在HashMap遍历中Key占据着主导地位,可以通过Key值找到对应的Value值//调用keySet()方法,Set<>泛型约束应与Key的数据类型一致//例如在本代码中,HashMap<Integer, String>,Key的数据类型为Integer,因此Set<>泛型约束也应当为Integer//Set<Integer> set11=hashMap.keySet();代码的意思为将HashMap中所有Key值存入Set集合(97,98,99,100)//那么set11即为Key值集合Set<Integer> set11=hashMap.keySet();//使用forEach()语句遍历,Integer为set11的数据类型,i为set11的复用名(相当于set11)//那么i就成为了Key值for(Integer i:set11){//在HashMap遍历中Key占据着主导地位,可以通过Key值找到对应的Value值//接下来我们要根据Key值来查找各个Key值对应的Value值//Value数据类型为String,设置一个String变量str来存储Value//hashMap.get(i);代码意思为根据i(Key值)找到相对应的Value值String str=hashMap.get(i);//打印输出System.out.println("Key的值为:"+i+" "+"Value的值为:"+str);}}
运行结果:
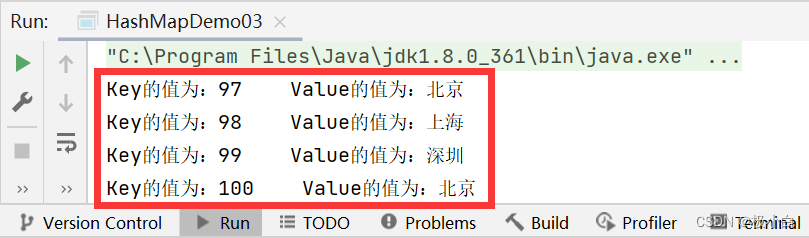
HashMap调用entrySet()方法遍历
public static void main(String[] args) {//若要使用HashMap,我们需要导入import java.util.HashMap;//我们使用泛型来约束HashMap的数据类型,Key为Integer数据类型,Value为String数据类型HashMap<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();//使用put()方法来添加数据hashMap.put(97, "北京");//第一对象hashMap.put(98, "上海");//第二对象hashMap.put(99, "广州");//第三对象hashMap.put(99, "深圳");//第四对象hashMap.put(100, "北京");//第五对象//调用entrySet方法遍历//调用entrySet()方法,Set<>泛型约束应与HashMap.Entry的数据类型一致,即<Integer, String>//<Key,Value>键值对,在Java语言中又被称之为Entry/entry,HashMap.Entry就相当于Student.name,若name的数据类型为String,则Student.name的数据类型为String,同理若<key,value>中key的数据类型为Integer,value的数据类型为String,则HashMap.Entry的数据类型为<Integer,String>,在这里就是<Integer, String>。//Set<HashMap.Entry<Integer,String>> set11=hashMap.entrySet();代码的意思为将HashMap中所有(Key,Value)值存入Set集合[(97,"北京"),(98,“上海”),(99,“深圳”),(100,“北京”)]//那么set11即为(Key,Value)值集合//同理我们也可写为Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> set11 = hashMap.entrySet();Set<HashMap.Entry<Integer, String>> set11 = hashMap.entrySet();//使用forEach()语句遍历,Integer为set11的数据类型,i为set11的复用名(相当于set11)//那么i就成为了(Key,Value)值for (HashMap.Entry<Integer, String> i : set11) {//打印输出,直接调用getKey()方法得到Key值,直接调用getValue()得到Value值System.out.println("Key的值为:" + i.getKey() + " " + "Value的值为:" + i.getValue());}}
运行结果:
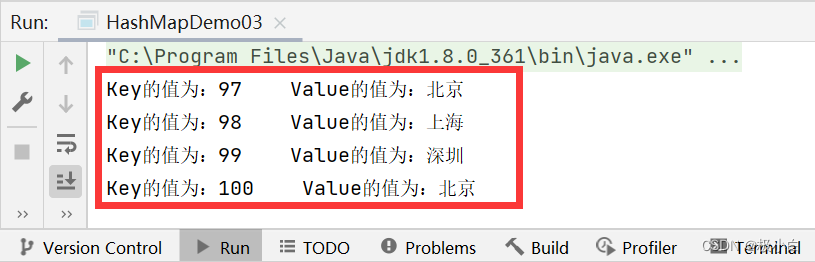 —
—
四、案例HashMap集合储存学生对象并遍历 HashMap基础强化
需求:创建一个Map集合,Key键是学生对象(Student),Value值是籍贯(String)。
要求:存储三个键值对元素(Entry),并遍历
Student类
public class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
HashMap遍历输出
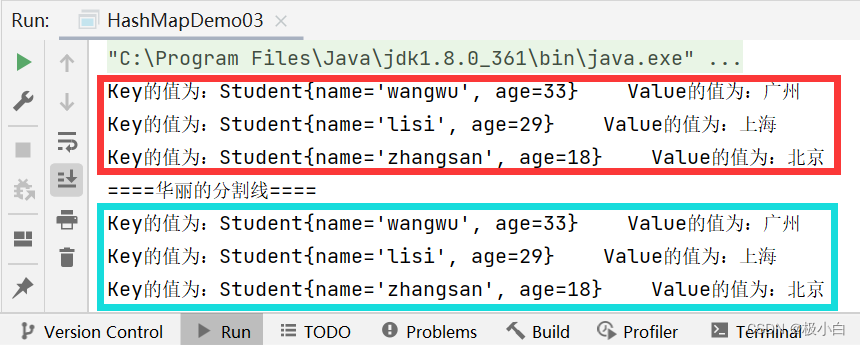
public static void main(String[] args) {//若要使用HashMap,我们需要导入import java.util.HashMap;//我们使用泛型来约束HashMap的数据类型,Key为Student数据类型,Value为String数据类型HashMap<Student, String> hashMap=new HashMap<>();//创建Student对象元素Student student1=new Student("zhangsan",18);Student student2=new Student("lisi",29);Student student3=new Student("wangwu",33);//使用put()方法来添加数据hashMap.put(student1,"北京");hashMap.put(student2,"上海");hashMap.put(student3,"广州");//调用keySet方法遍历//在HashMap遍历中Key占据着主导地位,可以通过Key值找到对应的Value值//调用keySet()方法,Set<>泛型约束应与Key的数据类型一致//例如在本代码中,HashMap<Student, String>,Key的数据类型为Student,因此Set<>泛型约束也应当为Student//Set<Student> set11=hashMap.keySet();代码的意思为将HashMap中所有Key值存入Set集合(student1,student2,student3)//那么set11即为Key值集合Set<Student> set11=hashMap.keySet();//使用forEach()语句遍历,Student为set11的数据类型,i为set11的复用名(相当于set11)//那么i就成为了Key值for(Student i:set11){//在HashMap遍历中Key占据着主导地位,可以通过Key值找到对应的Value值//接下来我们要根据Key值来查找各个Key值对应的Value值//Value数据类型为String,设置一个String变量来存储Value//hashMap.get(i);代码意思为根据i(Key值)找到相对应的Value值String str=hashMap.get(i);//打印输出System.out.println("Key的值为:"+i+" "+"Value的值为:"+str);}System.out.println("====华丽的分割线====");//调用entrySet方法遍历//调用entrySet()方法,Set<>泛型约束应与HashMap.Entry的数据类型一致,即<Student, String>//<Key,Value>键值对,在Java语言中又被称之为Entry/entry,HashMap.Entry就相当于Student.name,若name的数据类型为String,则Student.name的数据类型为String,同理若<key,value>中key的数据类型为Integer,value的数据类型为String,则HashMap.Entry的数据类型为<Integer,String>,在这里就是<Student, String>。//Set<HashMap.Entry<Student, String>> set22=hashMap.entrySet();代码的意思为将Map中所有(Key,Value)值存入Set集合[(Student("zhangsan",18),"北京"),(Student("lisi",29),“上海”),(Student("wangwu",33),“广州”)]//那么set22即为(Key,Value)值集合//同理我们也可写为Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> set22 = hashMap.entrySet();Set<HashMap.Entry<Student, String>> set22=hashMap.entrySet();//使用forEach()语句遍历,Integer为set22的数据类型,i为set22的复用名(相当于set22)//那么i就成为了(Key,Value)值for(HashMap.Entry<Student, String> i:set22){//打印输出,直接调用getKey()方法得到Key值,直接调用getValue()得到Value值System.out.println("Key的值为:"+i.getKey()+" "+"Value的值为:"+i.getValue());}}
运行结果:(我们发现输出顺序与插入顺序不一致,这是因为我们使用了Set集合来遍历Map,Set集合具有存取数据不一致的问题)
OK!!!结束!!!








