Unity 2-10 数据结构与算法
任务1-1:数据结构简介
数据结构:数据存储的结构,数据之间的关系
数据结构分类:
集合:同属于一个集合
线性结构:数据元素存在一对一的关系
树形结构:数据元素存在一对多的关系
图状结构:数据元素存在多对多的关系
算法:设计好的有限的确切的计算序列,所构成的完整的解题步骤,可以解决一类问题
数据结构和算法的关系:
数据结构是数据在程序中的存储结构和基本数据操作
算法是用来解决问题的,算法是基于数据结构的,数据结构是算法的基础
算法的评价标准:
运行时间:Time Consumption
占用空间:Space Consumption
很多时候时间和空间是需要trade off的;一般情况下运行时间是主要要考虑的
其他:正确性(Correctness)、可读性(Readability)、健壮性(Robustness)等
任务2-1:线性表 List-T
线性表:线性结构的抽象 -- 数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系
数据元素之间位置有顺序关系
c# 1.1 提供了一个非泛型接口 IList
实现了该接口的类有 ArrayList, ListDictionary, StringCollection, StringDictionary
c# 2.0 提供了泛型接口 IList<T>
实现了该接口的类有 List<T>
实例:
List<string> strList = new List<string>();
strList.Add("abc"); // add an element; index[0]
strList.Add("defg"); // index[1]
strList.Remove("defg"); // remove
strList.RemoveAt(int index);
strList.Count; // length = 1
strList.Clear(); // remove all data elements; length = 0
strList.Contains("abc"); // contains or not, returns a boolean
strList.CopyTo(string[] array); // copy all elements into an array
strList.IndexOf("abc"); // return the index of "abc" in the List
strList.Insert(1, "678"); // insert an element at index 1
strList.Sort(); // sort
任务2-2:实现自己的线性表 -- 定义线性表接口
线性表的接口定义:
interface IListDS<T> // DS表示Data Structure {int GetLength(); // Lengthvoid Clear(); // Clear all elementsbool IsEmpty(); // Is Empty or notvoid Add(T item); // Add an elementvoid Insert(T item, int index); // Insert an element at indexT Delete(int index); // delete an element with indexT this[int index] { get; } // 定义索引器 用来获取元素T GetEle(int index); // Get a particular elementint Locate(T value); // Get the index of the element }
线性表的实现方式:
顺序表、单链表、双向链表、循环链表
任务2-3&2-4:顺序表的实现
顺序表:线性表的顺序存储,在内存中用一块地址连续的空间依次存放数据元素:逻辑相邻且物理位置也相邻
知道顺序表的基地址(Base Addr)和每个元素的所占存储单元的大小,就可以求出任何一个数据元素的存储地址
C#中的数组在内存中占用的存储空间就是一组连续的存储区域,因此可用数组表示顺序表
![]()
顺序表优点:查找任何一个位置上的数据元素很方便
顺序表缺点:插入和删除时效率较低
using System; // Sequence List namespace _001_线性表 {/// 顺序表实现方式class SeqList<T>:IListDS<T>{private T[] data;//用来存储数据private int count = 0;//表示存了多少个数据// Constructorpublic SeqList(int size) {//size就是最大容量 data = new T[size];count = 0;}public SeqList():this(10) {//默认构造函数 容量是10 }/// 取得数据的个数public int GetLength() {return count;}// Clear all elementspublic void Clear() {count = 0;}// whether the sequence list is empty or notpublic bool IsEmpty() {return count == 0;}public void Add(T item) {if (count == data.Length) {// 当前数组已经存满 Console.WriteLine("当前顺序表已经存满");} else {data[count] = item;count++;}}public void Insert(T item, int index) {for (int i = count - 1; i >= index; i--) {data[i + 1] = data[i]; // 把数据往后移动 }data[index] = item;count++;}public T Delete(int index) {T temp = data[index];for (int i = index+1; i < count; i++) {data[i - 1] = data[i];// 把数据向前移动 }count--;return temp;}public T this[int index] {get { return GetEle(index); }}public T GetEle(int index) {if (index >= 0 && index <= count - 1) {// if the index is validreturn data[index];} else {Console.WriteLine("索引不存在");return default(T);}}public int Locate(T value) {for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {if (data[i].Equals(value)) {return i;}}return -1;}} }
任务2-5&2-6&2-7:单链表的实现
单链表:链式存储(Linked Storage)。
单链表的访问是单向的,只能访问下一个数据元素。
单链表的每一个数据元素由一个节点构成[data][next(pointer)]
需要有一个head节点来作为每次访问的开始
![]()
单链表优点:插入和删除时不需移动很多数据元素
单链表缺点:不可随机存储,查找某位置元素时需要遍历,效率较低
// 单链表的节点 namespace _001_线性表 {class Node<T> {private T data;//存储数据private Node<T> next;//指针,用来指向下一个元素// Constructorpublic Node() {// default value data = default(T);next = null;}public Node(T value) {data = value;next = null;}public Node(Node<T> next) {this.next = next;}public Node(T value, Node<T> next) {this.data = value;this.next = next;}// data的getter和setterpublic T Data {get { return data; }set { data = value; }}// next pointer的getter和setterpublic Node<T> Next {get { return next; }set { next = value; }} } }
namespace _001_线性表 {class LinkList<T> : IListDS<T> {private Node<T> head; // 头结点// Constructorpublic LinkList() {head = null;}public void Add(T item) {// create a new node to store the itemNode<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item);if (head == null) { // if the linkedlist is emptyhead = newNode;} else { // otherwise, get the tail of the linkedlistNode<T> current = head;while (current.Next != null) {current = current.Next;}// add the new node to the next of the tailcurrent.Next = newNode;}}public int GetLength() {int count = 0;if (head == null) { // if the linkedlist is emptyreturn count;}Node<T> current = head;count++;while (current.Next != null) {count++;current = current.Next;}return count;}public void Clear() {// 当清空后,没有引用指向头结点了,GC会自动回收// 头结点被回收后,没有引用指向第二个节点了,GC也会将它自动回收head = null;}public bool IsEmpty() {return head == null;}public void Insert(T item, int index) {Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item);// if index = 0; insert the item as the head nodeif (index == 0) {newNode.Next = head;head = newNode;} else { // otherwise, get the current pointer to index-1Node<T> current = head;for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {current = current.Next;}// insert the newNode between current and current.NextNode<T> preNode = current;Node<T> nextNode = current.Next;preNode.Next = newNode;newNode.Next = nextNode;}}public T Delete(int index) {// for the purpose of returning the deleted dataT deletedData = default(T);// if index = 0, remove the headif (index == 0) {deletedData = head.Data;head = head.Next;} else {// find the node of indexNode<T> current = head;for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {current = current.Next;}deletedData = current.Next.Data;Node<T> preNode = current;Node<T> nextNode = current.Next.Next;preNode.Next = nextNode;}return deletedData;}public T this[int index] {get {// find the node of indexNode<T> current = head;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {current = current.Next;}return current.Data;}}public T GetEle(int index) {return this[index];}public int Locate(T value) {// find the node of indexNode<T> current = head;if (current == null) {// if head is empty, the linkedlist is emptyreturn -1;}// otherwise, find the node of indexint index = 0;while (true) {if (current.Data.Equals(value)) {return index;} else {if (current.Next != null) {current = current.Next;} else {break;}}}return -1;}} }
任务2-8:双向链表和循环链表
双向链表:
节点有两个指针和一个数据 prev <- data -> next
与单链表比较的优点:单链表若要找某个节点的前驱节点,时间复杂度为O(n)
需要从表头引用开始遍历各节点,若某节点的Next等于该节点,则为该点的前驱节点
而双向链表对于该操作的时间复杂度为O(1)
Insert(T item, int index)示意图
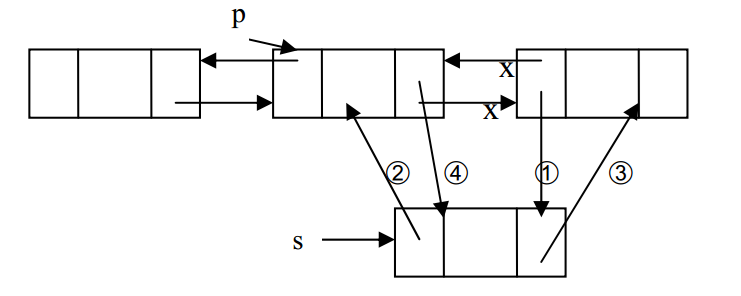
循环链表:Circular Linked List
没有明显的头尾节点,而需要方便地从最后一个节点访问到第一个节点
此时,最后一个节点的Next pointer指向的即为head节点
如果只有一个节点,则为一个head节点的Next指向自己
任务3-1:栈的介绍和BCL中的栈Stack
栈和队列:线性结构
与线性表的区别是:线性表的操作不受限制,而栈和队列的操作受到限制
可以把栈和队列视为操作受限的线性表
栈:Stack
操作限定在表的尾端进行的线性表 -- FILO (First In Last Out)
表尾称为栈顶Top,要进行插入、删除等操作
表头称为栈底Buttom,是固定的
空栈:Empty Stack:没有元素的栈

BCL (Basic Class Library)中的栈
Push() -- 入栈(添加数据到栈顶)
Pop() -- 出栈(删除栈顶数据,返回被删除的数据)
Peek() -- 取得栈顶数据,不删除
Clear() -- 清空栈
Count -- 取得栈中元素个数
Contains()/ CopyTo()/ ToArray() ...
实例:
Stack<char> stack = new Stack<char>();
stack.Push('a'); // a
stack.Push('b'); // ab
stack.Push('c'); // abc
Console.WriteLine(stack.Count); // 3
char temp = stack.Pop(); // 'c'
Console.WriteLine(stack.Count); // 2
temp = stack.Peek(); // 'b'
stack.Clear();
stack.Peek(); // 抛出异常 -- Peek()/ Pop()时需要检测空栈
任务3-2&3-3:实现自定义栈
栈的接口定义:
public interface IStackDS<T> {int Count {get;}int GetLength();bool IsEmpty();void Clear();void Push(T item);T Pop();T Peek(); }
栈的实现方式:顺序栈Sequence Stack、链栈
顺序栈:
用连续的存储空间来存储栈中的数据元素
类似于顺序表,用一位数组来存放顺序栈中的数据元素
空栈时top为index=-1;有一个元素时top为index=0;
class SeqStack<T> : IStackDS<T> {private T[] data;private int top; // 指向栈顶的indexpublic SeqStack(int size) {data = new T[size];top = -1;}public SeqStack() : this(10) {// default size = 10 }public int Count {get {return top + 1;}}public int GetLength() {return Count;}public bool IsEmpty() {return (Count == 0);}public void Clear() {top = -1;}public void Push(T item) {if (top == (data.Length - 1)) {// 栈满Console.WriteLine("栈满,无法Push");} else {data[top+1] = item;top++;}}public T Pop() {T topItem = data[top];top--;return topItem;}public T Peek() {return data[top];} }
链栈:
链栈节点的结构与单链表节点的结构一样。
哪一边设置为链栈的头部呢?为了操作方便,把栈顶设在链表的头部
Push():新数据指向原头结点,head指向新数据
Pop():head指向head.Next
namespace _002_栈 {/// 链栈的结点 class Node <T>{private T data;private Node<T> next;public Node() {data = default(T);next = null;}public Node(T data) {this.data = data;next = null;}public Node(T data, Node<T> next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}public Node(Node<T> next) {data = default(T);this.next = next;}public T Data {get { return data; }set { data = value; }}public Node<T> Next {get { return next; }set { next = value; }}} }
任务3-4:队列的介绍和BCL中的队列Queue
队列:Queue:插入操作被限定在表的尾部,而其他操作被限定在表的头部的线性表
进行插入操作的表尾称为队尾(Rear),进行其他操作的头部称为队头(Front)
队列中没有数据元素时称为空队列(Empty Queue)
FIFO (First In First Out)

BCL中的队列:实例
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
queue.Enqueue(23); // 入队,23
queue.Enqueue(45); queue.Enqueue(67); queue.Enqueue(89); // 23, 45, 67, 89
Console.WriteLine(queue.Count); // 4
queue.Dequeue(); // 出队,23,Count = 3
int j = queue.Peek(); // 取得队首值 45,Count = 3
queue.Clear(); // 清空 Count = 0
任务3-5:自定义队列接口
namespace _003_队列 {interface IQueue<T> {int Count { get; } // 取得队列长度的属性int GetLength(); // 求队列的长度bool IsEmpty(); // 判断队列是否为空void Clear(); // 清空void Enqueue(T item); // 入队T Dequeue(); // 出队T Peek(); // 取得队首元素 } }
队列的实现方式:顺序队列、链队列
任务3-6&3-7:自定义顺序队列的实现
顺序队列:Sequence Queue,用物理连续的存储空间来存储队列中的数据元素
类似于顺序栈,用一维数组来存放顺序队列中的数据元素
队首index=0,用front表示,front=0-1=-1;队尾用rear表示
当队列为空时,front = rear = -1
插入一个数据时,rear++; 删除一个数据时,front++;
假溢出:队首元素被删除后留下了空位,队尾不断添加直到队列一端满了
--> 循环顺序队列:队列的队尾满后,继续从index=0的位置开始存储,称为一个循环
class SeqQueue<T> : IQueue<T> {private T[] data;private int count; // 表示当前有多少个元素private int front; // 队首 (队首元素索引-1)private int rear; // 队尾(=队尾元素索引)public SeqQueue(int size) {data = new T[size];count = 0;front = -1;rear = -1;}public SeqQueue() : this(10) {// default size = 10 }public int Count {get { return count; } }public int GetLength() {return count;}public bool IsEmpty() {return count == 0;}public void Clear() {count = 0;front = -1;rear = -1;}public void Enqueue(T item) {// check whether the queue is filledif(count == data.Length) {Console.WriteLine("队列已满");} else {if (rear == data.Length-1) {// 刚好假溢出rear = 0;} else {// rear < front的假溢出// 或是front < rear的正常情况rear++;}data[rear] = item;count++;}}public T Dequeue(){if(count==0) {// empty queueConsole.WriteLine("Empty queue, Dequeueing denied");return default(T);} else {T temp = data[front + 1];front++;if (front == data.Length - 1) {// 循环一轮了front = -1;}count--;return temp;}/* 老师源码,没有考虑到循环一轮的情况if (count > 0) {T temp = data[front + 1];front++;count--;return temp;} else {Console.WriteLine("队列为空,无法取得队首的数据");return default(T);}*/}public T Peek() {return data[front + 1];} }
任务3-8:链队列的实现
链队列:Linked Queue,链队列通常用单链表来表示,可以看作是单链表的简化。
链队列的节点与单链表一样。
class Node <T> {private T data;private Node<T> next;public Node(T data) {this.data = data;}public T Data {get { return data; }set { data = value; }}public Node<T> Next {get { return next; }set { next = value; }} }
class LinkQueue <T>:IQueue<T> {private Node<T> front; // 头节点 private Node<T> rear; // 尾结点private int count; // 表示元素的个数public LinkQueue() {front = null;rear = null;count = 0;}public int Count {get { return count; }}public int GetLength() {return count;}public bool IsEmpty() {return count == 0;}public void Clear() {front = null;rear = null;count = 0;}public void Enqueue(T item) {Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item);if (count == 0) {// empty queuefront = newNode;rear = newNode;} else {rear.Next = newNode;rear = newNode;}count++;}public T Dequeue() {if (count == 0) {// empty queueConsole.WriteLine("Empty Queue, Dequeueing Denied");return default(T);} else if (count == 1) {T data = front.Data;front = null;rear = null;count--;return data;} else {T data = front.Data;front = front.Next;count--;return data;}}public T Peek() {if (front != null) {return front.Data;} else {return default(T);}} }
任务3-9:栈和队列的应用
1. 判断一个字符串是否为回文。
将字符串分别放入队列和栈,并逐个出队列和出栈比较即可
static void Main(string[] args) {string str = Console.ReadLine();Stack<char> stack = new Stack<char>();Queue<char> queue = new Queue<char>();bool isHuiwen = true;for (int i = 0; i < str.Length; i++) {stack.Push(str[i]);queue.Enqueue(str[i]);}while (stack.Count > 0 && queue.Count > 0) {if (!stack.Pop().Equals(queue.Dequeue())) {isHuiwen = false;break;}}if (isHuiwen) {Console.WriteLine("是回文");}else {Console.WriteLine("不是回文");}Console.ReadKey(); }
任务4-1&4-2:实现自定义字符串类
class StringDS {private char[] data;//用来存放字符串中的字符public StringDS(char[] array) {// copy from array to datadata = new char[array.Length];for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++) {data[i] = array[i];}}public StringDS(string str) {// copy from string to datadata = new char[str.Length];for (int i = 0; i < data.Length; i++){data[i] = str[i];}}//根据索引访问字符的索引器// 模仿string,string内字符是不可以修改的,因此不用写setpublic char this[int index] {get { return data[index]; }}public int GetLength() {return data.Length;}// 如果两个字符串一样 那么返回0// 如果当前字符串小于s,那么返回-1// 如果当前字符串大于s,那么返回1public int Compare(StringDS s) {// get the length of the shorter stringint len = this.GetLength() < s.GetLength() ?
this.GetLength() : s.GetLength();for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {if(this[i] < s[i]) {return -1;} else if(this[i]>s[i]) {return 1;} else {// this[i] == s[i] }}// two strings are the same// or the shorter string is the substring of the longer oneif(this.GetLength() == s.GetLength()) {return 0;} else {if(this.GetLength() < s.GetLength()) {// this is shorterreturn -1;} else {return 1;}}}public StringDS SubString(int index, int length) {char[] subChars = new char[length];for(int i = index;i<length+index;i++) {subChars[i - index] = data[i];}return new StringDS(subChars);}public static StringDS Concat(StringDS s1, StringDS s2) {//s1 0- s1.leng-1char[] concatString = new char[s1.GetLength()+s2.GetLength()];for (int i = 0; i < s1.GetLength(); i++) {concatString[i] = s1[i];}for (int i = s1.GetLength(); i < concatString.Length; i++) {concatString[i] = s2[i - s1.GetLength()];}return new StringDS(concatString);}public int IndexOf(StringDS s) {for(int i = 0; i <= this.GetLength() - s.GetLength(); i++) {bool isEqual = true;for(int j = 0; j < s.GetLength(); j++) {if(this[i+j] != s[j]) {// Console.WriteLine(this[i+j] + " " + s[j]);isEqual = false;break;}}if (isEqual) {return i;}}return -1;} }
任务4-3:数组
数组的特点:数组中的数据元素可以是具有某种结构的数据,但需要属于同一数据类型。
C#的所有数组都继承自System.Array
Array是一个抽象类,本身继承自System.Object
因此,数组是在托管堆上分配空间,是应用类型
任何数组变量包含的是一个指向数组的引用,而非数组本身
当数组中的元素为值类型时,该类型所需的内存空间也作为数组的一部分来分配 (如int)
当数组中的元素是引用类型时,数组包含的只是引用 (如string[])
Array类中常用方法:
bool isFixedSize; // 数组的大小是不可变的,因此是true
int Length; // 元素的个数(数组的长度)
int Rank(); // 获取Array的秩(维度)
static int BinarySearch(Array arr, object value); // 在arr中二分查找value
static int BinarySearch(Array arr, int index, int length, object value); // 加入了范围
static void Clear(Array arr, int index, int length); // 清空,设置为0/ false/ null
object Clone(); // 复制全部元素
static void Copy(Array sourceArr, Array destArr, int length); // 从头开始复制length个元素
void CopyTo(Array arr, int index); // 从index个元素开始复制
int GetLength(int dimension); // 获取指定维数中的元素个数
object GetValue(int index); // 返回index处的值
static int IndexOf(Array arr, obejct value); // 返回value在arr中第一个匹配项的index
static int LastIndexOf(Array arr, object value); // 返回value在arr中最后一个匹配项的index
static void Reverse(Array array); // 反转该数组
static void Sort(Array array); // 对数组中的值进行快速排序
任务4-4:字符串练习题
问题:
1. 设 s=”I am a teacher”,i=”excellent”,r=”student”。用 StringDs类中的方法求:
( 1) 串 s、i、r 的长度;
( 2) s.SubString(8, 4)、i.SubString(2, 1);
( 3) s.IndexOf(“tea”)、i.IndexOf(“cell”)、r.IndexOf(“den”)。
2. 字符串的替换操作是指:已知字符串 s、t、r,用 r 替换 s 中出现的所有与 t 相等的子串。
写出算法,方法名为 Replace。
答案:
1. s.GetLength(); i.GetLength(); r.GetLength(); // 14, 8,
s.SubString(8, 4); // each
i.SubString(2, 1); // c
s.IndexOf(new StringDS(“tea”)); // 7
i.IndexOf(new StringDS(“cell”)); // 2
r.IndexOf(new StringDS(“den”)); // 3
2. 用IndexOf(t)取得s中第一个相符的子串,用r替换;
重复第一步,直到没有IndexOf(t)返回-1为止
任务5-1:排序介绍
排序:把一个记录集合或序列重新排列成按记录的某个数据项递增/递减的序列
作为排序依据的数据项称为排序项,也成为记录的关键码 (Keyword).
关键码分为主关键码 (Primary Keyword)和次关键码 (Secondary Keyword)
主关键码对于每一个记录来说都不一样,排序结果是唯一的;而次关键码可能相同
当记录中可能存在具有相同关键码值的记录时,这些记录在排序结果中,如果使用某个排
序方法对任意的记录排序后相同关键码值的记录之间的位置关系与排序前一致,则称
此排序方法是稳定的,否则是不稳定的
由于待排序的记录的数量不同,使得排序过程中涉及的存储器不同,可将排序方法分为
内部排序 (Internal Sorting) 和外部排序 (External Sorting)两大类
内部排序:排序的整个过程中,记录全部存放在内存中,并且在内存中调整记录之间
的相对位置,在此期间没有进行内、外存的数据交换;
外部排序:在排序过程中,记录的主要部分存放在外存中,借助于内存逐步调整记录
之间的相对位置,在这个过程中,需要不断在内、外存之间交换数据。
任务5-2:直接插入排序
将一个数据插入已经排好序的有序数据中,从而得到一个新有序数组,适用于少量数据的排序
将待排序数组分成两部分:1. 第一个元素,2. 除了第一个元素之外的其他所有元素
时间复杂度为 O(n^2)
是稳定的排序方法
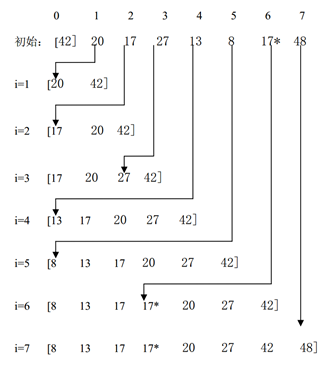
0. [42]为有序数列,之后的为待排序数列
1. 20与之前的有序数列[42]比较,比较大的便外后移 [20,42]
2. 17与之前的有序数列[20,42]比较,比较大的便外后移[20,17,42], [17,20,42]
3. 27与之前的数列[17,20,42]比较,比较大的后移[17,20,27,42]
4. ...
5.
任务5-3:简单选择排序
任务5-4&5-5&5-6:快速排序








