接着上篇博客的代码继续写
1.接口版本控制
一个系统上线后会不断迭代更新,需求也会不断变化,有可能接口的参数也会发生变化,如果在原有的参数上直接修改,可能会影响线上系统的正常运行,这时我们就需要设置不同的版本,这样即使参数发生变化,由于老版本没有变化,因此不会影响上线系统的运行。
一般我们可以在地址上带上版本号,也可以在参数上带上版本号,还可以再 header 里带上版本号,这里我们在地址上带上版本号,大致的地址如:http://api.example.com/v1/test,其中,v1 即代表的是版本号。具体做法请看代码:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.Mapping;import java.lang.annotation.*;/*** 版本控制* @author XIHONGLEI* @date 2018-11-15*/ @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Mapping public @interface ApiVersion {int value(); }
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestCondition;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern;/*** @author XIHONGLEI* @date 2018-11-15*/ public class ApiVersionCondition implements RequestCondition<ApiVersionCondition> {// 路径中版本的前缀, 这里用 /v[1-9]/的形式private final static Pattern VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("v(\\d+)/");private int apiVersion;public ApiVersionCondition(int apiVersion) {this.apiVersion = apiVersion;}@Overridepublic ApiVersionCondition combine(ApiVersionCondition other) {// 采用最后定义优先原则,则方法上的定义覆盖类上面的定义return new ApiVersionCondition(other.getApiVersion());}@Overridepublic ApiVersionCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {Matcher m = VERSION_PREFIX_PATTERN.matcher(request.getRequestURI());if (m.find()) {Integer version = Integer.valueOf(m.group(1));if (version >= this.apiVersion) {return this;}}return null;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(ApiVersionCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {// 优先匹配最新的版本号return other.getApiVersion() - this.apiVersion;}public int getApiVersion() {return apiVersion;} }
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition.RequestCondition; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/*** @author XIHONGLEI* @date 2018-11-15*/ public class CustomRequestMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping {@Overrideprotected RequestCondition<ApiVersionCondition> getCustomTypeCondition(Class<?> handlerType) {ApiVersion apiVersion = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, ApiVersion.class);return createCondition(apiVersion);}@Overrideprotected RequestCondition<ApiVersionCondition> getCustomMethodCondition(Method method) {ApiVersion apiVersion = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, ApiVersion.class);return createCondition(apiVersion);}private RequestCondition<ApiVersionCondition> createCondition(ApiVersion apiVersion) {return apiVersion == null ? null : new ApiVersionCondition(apiVersion.value());} }
#然后在WebConfig配置类中注入Beanimport com.hello.config.CustomRequestMappingHandlerMapping; import com.hello.filter.ApiInterceptor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping;/*** 配置类* @author XIHONGLEI* @date 2018-10-31*/ @SpringBootConfiguration public class WebConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {@Overrideprotected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {super.addInterceptors(registry);// 将 ApiInterceptor 拦截器类添加进去registry.addInterceptor(new ApiInterceptor());}@Override@Beanpublic RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {RequestMappingHandlerMapping handlerMapping = new CustomRequestMappingHandlerMapping();handlerMapping.setOrder(0);handlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());return handlerMapping;} }
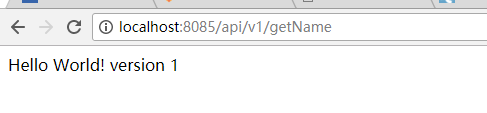
#最后定义一个带版本控制的接口 import com.hello.WebConfig; import com.hello.config.ApiVersion; import com.hello.entity.ContractDetailDto; import com.hello.service.CheckPositionService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import java.util.List;@RestControllerpublic class HelloController {@Autowiredprivate WebConfig webConfig;@ApiVersion(1)@RequestMapping("{version}/getName")public String vGetName() {return "Hello World! version 1";}@ApiVersion(2)@RequestMapping("{version}/getName")public String getName() {return "Hello World! version 2";} }
查看效果:

2.模板引擎
在传统的 SpringMVC 架构中,我们一般将 JSP、HTML 页面放到 webapps 目录下面,但是 Spring Boot 没有 webapps,更没有 web.xml,如果我们要写界面的话,该如何做呢?
Spring Boot 官方提供了几种模板引擎:FreeMarker、Velocity、Thymeleaf、Groovy、mustache、JSP。
这里以 FreeMarker 为例讲解 Spring Boot 的使用。
首先引入 FreeMarker 依赖:
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-freemarker</artifactId></dependency>
在 resources 下面建立两个目录:static 和 templates,如图所示:

其中 static 目录用于存放静态资源,譬如:CSS、JS、HTML 等,templates 目录存放模板引擎文件,我们可以在 templates 下面创建一个文件:index.ftl(freemarker 默认后缀为 .ftl),并添加内容:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Hello ${name}!</title> </head> <body>Hello ${name}! </body> </html>
然后在POM中配置Resource的时候一定要把所有的资源文件都包括:
<resources><resource><directory>src/main/java</directory><includes><include>**/*.yml</include><include>**/*.properties</include><include>**/*.xml</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource><resource><directory>src/main/resources</directory><includes><include>**/*</include></includes><filtering>false</filtering></resource></resources>
新建Contrlller:
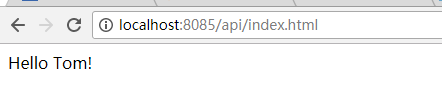
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;@Controller public class HomeController {@RequestMapping(value = "/index")public ModelAndView index() {ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView("/index");view.addObject("name","Tom");return view;} }
看结果: